Inflamed gums
- Treatments /
- Inflamed gums
Would you like to become our patient?
Schedule your initial consultation today and begin your journey to a painless, healthier smile. Contact us now!
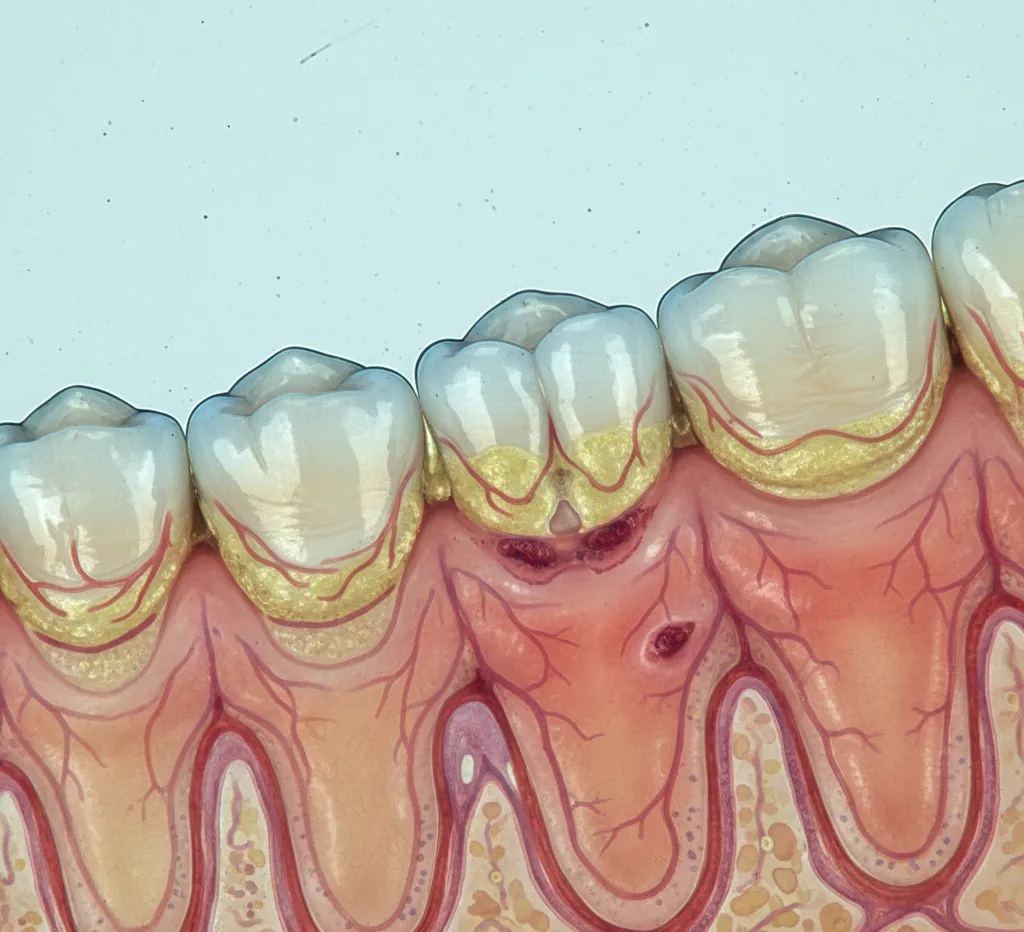
De kleur van gezond tandvlees is roze. Ontstoken tandvlees Den Haag is vaak roder van kleur, gezwollen en bloedt sneller bij bijvoorbeeld tandenpoetsen. Er is een regel die altijd geldt: gezond tandvlees bloedt nooit! Het eerste stadium van ontstoken tandvlees wordt gingivitis genoemd, een verder gevorderd stadium noemen we parodontitis.
Development of inflamed gums.
De ontsteking in de rand van het tandvlees wordt veroorzaakt door bacteriën in de tandplak. Tandplak is een zacht en kleverig, nauwelijks zichtbaar laagje van speekseleiwitten en bacteriemassa (biofilm) op de tanden en kiezen. Tandplak kan verkalken tot tandsteen dat stevig vastzit aan de tanden en kiezen. Hierop wordt weer een nieuw laagje plak gevormd etc.
Symptoms of inflamed gums.
Inflamed gums aren't always clearly visible. Some symptoms that may occur include red, soft, and swollen gums and/or bleeding gums when brushing. A bad taste or bad breath can also indicate inflamed gums. Inflamed gums rarely cause pain.
Consequences of inflamed gums.
De ontsteking ontstoken tandvlees Den Haag in de tandvleesrand kan zich uitbreiden in de richting van het kaakbot. Het tandvlees laat daardoor los van de tanden en kiezen. De ruimte die zo ontstaat, noemen we een verdiepte pocket. In de ruimte tussen het tandvlees en de tanden en kiezen vormt zich weer tandplak. Door deze tandplak verplaatst de ontsteking zich nog verder in de diepte. De vezels gaan door de ontsteking kapot en het kaakbot wordt afgebroken. Hierdoor worden de pockets dieper. In de verdiepte pockets verkalkt de tandplak gedeeltelijk tot tandsteen. Deze voortschrijdende ontsteking met afbraak van vezels en kaakbot heet parodontitis. Eenmaal afgebroken kaakbot kan zich niet meer herstellen.
Preventing and curing inflamed gums.
Gum inflammation is preventable and treatable. Good oral hygiene is essential for this. Bleeding gums indicate gum inflammation. Don't ignore this sign; take action to restore your gums to a healthy state. Plaque is the cause of gum inflammation. Therefore, it's important to keep your mouth clean. Tools for cleaning your mouth include: (electric) toothbrushes, toothpaste, toothpicks, dental floss, interdental brushes, gauze, and/or a tongue scraper. Always consult your dentist or dental hygienist about which tools are most suitable for you.
Advanced inflamed gums: periodontitis.
Between the teeth and gums lies a space called a pocket. Healthy pockets are shallow and non-bleeding. Gum inflammation can spread deeper into the jawbone surrounding the teeth. These pockets can then deepen due to bone loss around the roots of a tooth. This is called periodontitis: an advanced inflammation of the gums and the supporting tissues surrounding a tooth.
Source: Dutch Association for Periodontology
- FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Orthodontics is a dental specialty that focuses on diagnosing, preventing, and treating dental and facial abnormalities, such as crooked teeth and jaws.
Dental sealants are thin, protective layers applied to the chewing surfaces of teeth to prevent cavities.
Yes, teeth whitening treatments performed by a dentist or with dentist-approved products are safe and effective.
Cosmetic dentistry focuses on improving the appearance of teeth, gums, and smile through treatments such as whitening, veneers, and bonding.
Home whitening options include whitening strips, gels, toothpaste, and custom-made trays prescribed by your dentist.
📞 Contact Dental
Care Statenkwartier
Do you have a question, would you like to change an appointment, or would you like more information about our treatments?
Complete the form and click “Send.”
We will respond as quickly as possible—usually within one business day. You can also contact us by phone or email e-mail reaches.